Rocket launches are costly and laborious, however for many years they’ve been the worth of doing enterprise for area businesses hoping to get their newest satellite tv for pc, telescope, or staff of astronauts into the good blue yonder.
However new missions and mission ideas are getting ready for a courageous new world, one through which humankind has a longtime, semi-permanent presence off-Earth. It begins with the Moon, the place people haven’t been for 51 years. However as soon as we learn to have a sustainable, long-term presence there, the good expanse past appears way more attainable.
Human transit to and habitation of different worlds and satellites is a part of the equation. One other a part of the equation is constructing experiments and infrastructure that harnesses the encircling setting, a course of known as in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU.
How we are going to get to and make use of the cosmos are basic questions in our pursuit of higher understanding it. As we step out from our blue marble and check the waters (or regolith) past, scientists will develop new methods of understanding the universe. Gizmodo took a while to talk with technologists, engineers, and theorists who work on applied sciences that may make our scientific investigation of area simpler.
Why do we have to do science in area?
There are observatories on Earth that have a look at the cosmos and its quirky phenomena, from telescopes that observe ancient light to super-sensitive detectors that really feel reverberations of gravitational ripples in spacetime. So why do science in area?
For one, it’s laborious to see area from Earth. Skyglow from mild air pollution is making it more and more tough to see the celebrities, in accordance with research published earlier this year. However skyglow apart, our planet was not optimizing for astronomical observations because it took form over the past 4.6 billion years.
“There’s an enormous fraction of the electromagnetic spectrum that you simply’re blind to from the floor of the Earth,” mentioned Paul Goldsmith, an astronomer at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in a video name with Gizmodo. “The very environment—particularly the water and oxygen in our environment that allow us stay right here—are what makes life difficult for astronomers.”
Accordingly, area businesses launch observatories which might be suspended in orbit. That started with OAO-2, the primary profitable area telescope and the ancestor of all trendy area telescopes. However now, the Webb House Telescope takes in far- and near-infrared mild a million miles from Earth and the Chandra X-ray Observatory orbits Earth tens of hundreds of miles from the planet to avoid the worst of its radiation.
However there may be solely a lot science we will do with observations from afar, even these achieved by essentially the most keen-eyed astronomical devices. Think about the Moon: finding out the lunar regolith and mapping its craters by a telescope provide clues on its formation and make-up, however analyzing lunar samples (particularly these collected in the course of the Apollo missions and, extra just lately, China’s Chang’e-5 lander) give scientists priceless insights into the makeup of lunar gasses and how the Moon might hold water. And on Mars, the Perseverance rover is actively accumulating rock samples to finally ship to Earth as a part of the Mars Sample Return mission. These samples will probably be probed for hints as to Mars’ geological historical past, but additionally proof that the Purple Planet could have as soon as supported historic microbial life.
The seek for life—even indicators of historic life—past Earth is a quest of paramount significance. If we have been to seek out indicators that life does, or did, exist past our personal world, it might permit us to ask critical questions in regards to the ethics of exploring area and the implications of us not being alone within the universe in a fabric manner (we’ve been asking these questions hypothetically for a very long time now). If indicators of life have been discovered past Earth, it might additionally change the sorts of missions that area businesses and business entities would prioritize.
In fact, it might be simpler—and in the long term, arguably cheaper—to have a longtime, sustainable human presence exploring Mars on its floor than to frequently launch autos to the planet to retrieve samples like these being collected by Perseverance.
The deliberate Artemis missions could showcase that concept on the Moon. Regardless of their identify, the Artemis missions will not be actually the dual of the Apollo missions. Apollo’s function was to go to and take samples of the Moon, after which get all of the astronauts again to Earth in a single piece. Artemis will set the foundations for a sustained human presence on the Moon, from infrastructure on the lunar floor to the Lunar Gateway, an area station that may help astronauts in orbit of our rocky satellite tv for pc because the Worldwide House Station does Earth.
Simpler entry to the ultimate frontier
Crucially, the prices of rocket launches—the biggest barrier to getting new missions into area, by Goldsmith’s measure—are falling. 2023 is seeing an enormous number of rocket launches and reusable rockets will make much more launches potential for much less value. SpaceX’s reusable Falcon 9, for instance, is chargeable for almost half of all orbital launches this 12 months to this point, according to Gunter’s Space Page.
“It’s important to hope that the automobile to get it there isn’t vastly costly or else the entire thing turns into unaffordable,” Goldsmith mentioned. “So the hope is that the business area prices dropping will get you into area and/or to the floor of the Moon in a manner which you could put extra of the cash into the payload and do thrilling science relatively than largely paying to easily get there.”
And as rocket prices fall, their energy and carrying capacities are on the rise. Think about Starship, SpaceX’s in-growth megarocket, which is anticipated to usurp the corporate’s Falcon 9 as SpaceX’s marquee launch automobile.
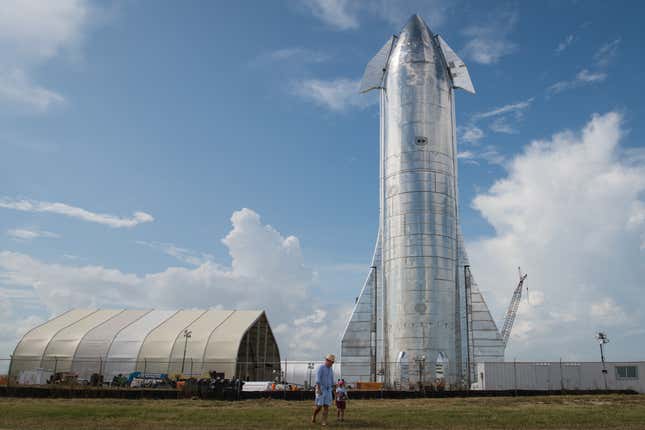

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) generates 8.8 million kilos of thrust at launch; the 400-foot-tall Starship, against this, will exert 16.5 million kilos of thrust. And as beforehand reported by Gizmodo in our exhaustive (no pun intended) guide on the brand new rocket, Starship will be capable of cary 330,000 kilos (150 metric tons) of payload to low Earth orbit inside its outsized payload fairing.
Merely put: Starship is poised to ship heavier and greater gear to area, that means scientists and engineers will be capable of embrace extra bells and whistles to their future mission ideas. For sure, the bounds of a mission idea will at all times be constrained by what can really be launched into area. That mentioned, in-space manufacturing—a functionality at present on the horizon—will allow the event of profoundly extra advanced space-based instruments.
On the identical time, new applied sciences are enhancing our means to watch the cosmos. The Webb House Telescope, a $10 billion area observatory launched in December 2021, has already produced a year’s worth of scientific imagery, in addition to copious quantities of information on distant molecular clouds and the prevalence of habitable worlds, amongst many different strains of inquiry.
The Webb House Telescope had a complete payload mass of 13,670 kilos. Whereas a mission’s mass is under no circumstances an indicator of its affect, fewer limits on mission payloads (courtesy of Starship) will imply extra alternatives to strap up a rocket with scientific gear.
Webb is positioned at L2, a area in area about a million miles from Earth that enables the telescope to picture the universe with minimal gas burn. At such a distance, L2 can be spared mild air pollution from Earth and the glut of satellite constellations placing streaks of sunshine in different observatories’ photographs.
Mockingly, the identical firm that’s creating the rocket of spaceflight’s future is chargeable for clogging up low-Earth orbit. Based on statistics saved by Harvard-Smithsonian astrophysicist Jonathan McDowell, HouseX has launched 5,048 Starlink web satellites to this point, of which 4,670 are at present operational.
It’s laborious to say exactly what the long run purposes of megaconstellations will probably be, however astronomers are increasingly worried about how the units will mess with telescopic observations. Scientists have developed software that may edit streaks of sunshine from satellites out of their imagery, however that appears extra like a stopgap measure than a panacea.
On Earth, units just like the largest digital camera ever built will assist scientists see the sky higher than ever, regardless of the environment. The upcoming 3.2-gigapixel digital camera would be the cornerstone of the Vera Rubin Observatory’s Legacy Survey of Space and Time, a 10-year survey that may picture the evening sky each 15 seconds, taking a whole portrait of the southern sky about as soon as every week. Excessive in Chile’s Atacama Desert, the digital camera will take care of little mild air pollution and fewer atmospheric perturbations than different Earth-based telescopes.
With new applied sciences innovating the best way we see the cosmos and falling costs on rocket launches, scientific missions will be launched extra regularly, hastening the speed of discovery.
What’s the way forward for science in area?
A key query surrounding science missions past Earth is who, or what, will construct them. House is inhospitable to people, with intense temperature adjustments, radiation, no breathable air to talk of, and no instantly accessible sources of meals or water. The reply, due to this fact, is robots. We’ve developed robots that fly on Mars and that drill into the planet’s rocky history, so why not ship extra robots into area to do the work that people can’t, or maybe mustn’t?
Angelo Vermeulen, a biologist and area techniques researcher at Delft College of Know-how within the Netherlands, mentioned that folks within the area—erm, area—typically see the 2 sorts of explorer as mutually unique, and it’s a “considerably charged” matter within the area group.
“I believe it’s slightly unlucky that typically it results in a dialogue like this as a result of it’s most likely each,” Vermeulen advised Gizmodo in a video name. “As you’ll be able to think about, having people on the market with robotic companions looks as if the most effective of each worlds.”
Vermeulen is a co-author on a paper just lately published in Frontiers in Astronomy and House Science exploring bioregenerative life help techniques—that’s, techniques that may alter and adapt themselves over the course of a journey by area.
“We don’t want to find some new legal guidelines of physics to kickstart interstellar exploration,” Vermeulen mentioned. “Between 40 and 100 years, it’s best to be capable of attain [the nearest stars]. And so we enter the area of multigenerational area journey, which has its personal units of challenges—together with moral, in fact, I’m not shying away from that.”
The identical sorts of techniques designed for Vermeulen’s Evolving Asteroid Starships mission might be utilized to a a lot nearer goal than the closest stars: the Moon. NASA plans to get humans back on the Moon inside this decade, so designing techniques that make a sustained human presence potential on our chilly, atmosphere-less satellite tv for pc are of utmost significance. And no entity is doing extra to deal with these questions than the NASA Revolutionary Superior Ideas (NIAC) program, the testing floor for scientific experiments off-Earth.
NIAC produces a steady stream of funded projects to enhance humankind’s means to journey past Earth and examine the cosmos. From studying the best way to remodel Martian soil into arable land to utilizing lasers to propel spacecraft, NIAC proposals work to resolve issues that haven’t but grow to be issues, in order that humankind is prepared for after they come up.
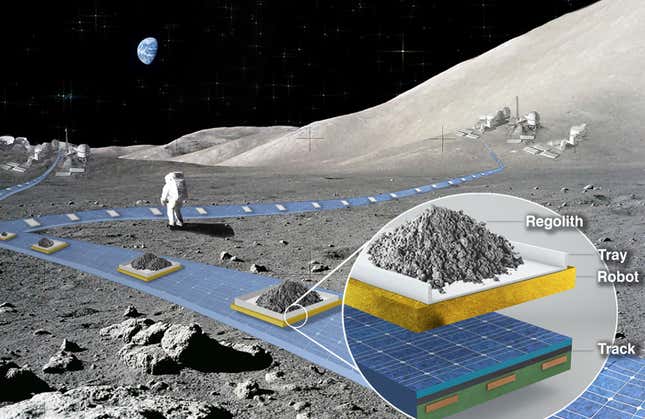

One such design is the Flexible Levitation On A Track (FLOAT) proposal, which is a magnetic levitation system that might assist transfer lunar regolith (or different heavy issues on the Moon). The system is designed to function like a floating conveyor belt, delivery mined supplies on the lunar floor with out having to fret in regards to the uneven lunar floor. Ethan Schaler, FLOAT’s principal investigator (and likewise the principal investigator of the SWIM NIAC idea, and a robotic techniques engineer for NASA’s Perseverance mission on Mars), mentioned that designing a mission is (sort of) enjoyable and video games whenever you’re engaged on an idea. “The satan is at all times within the particulars whenever you begin constructing the flight {hardware},” Schaler advised Gizmodo in a video name.
Associated article: Will Mining the Moon and Asteroids Be Worth the Trouble?
“I’m an optimist on analysis; I like eager about cool new concepts and the way they may work,” Schaler added, “and I’m a realist in the case of precise missions. And whenever you’re working a mission, you must take into consideration each manner it might go improper and design methods to keep away from all of them.”
A levitating observe for carrying heavy materials off-Earth is only one NIAC mission idea designed with the Moon in thoughts. Some sound much more sci-fi: take into account the Lunar Crater Radio Telescope (LCRT), a NIAC mission idea which goals to show a crater on the far facet of the Moon right into a detector for ultra-long-wavelength radio waves emanating from the universe’s Dark Ages.
“The explanation why the Darkish Ages are a very good time to take a look at darkish matter and matter’s interplay is as a result of there may be nothing else [happening]. The second the primary stars are born…you lose all of the signatures of darkish power,” mentioned Saptarshi Bandyopadhyay, a robotics technologist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and a member of the LCRT staff, in a video name with Gizmodo.
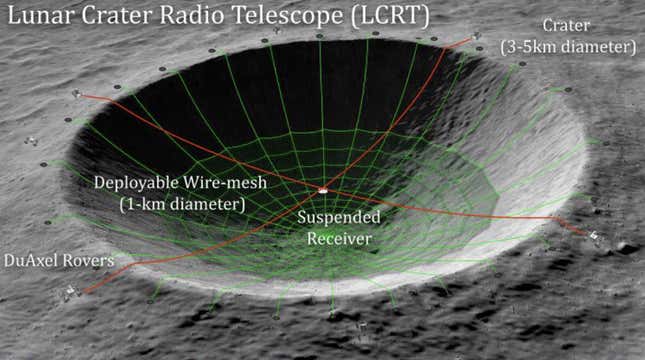
Being situated on the far facet of the Moon would imply that the telescope’s information would want to get beamed as much as an orbiter that will then transmit the information to Earth.
“LCRT has a double drawback,” mentioned Goldsmith, who can be a member of the LCRT mission. “One is whenever you go to very, very, very low frequencies, the Earth’s ionosphere begins blocking the alerts. And then you definately even have the issue that the interference from all of the transmissions from the whole lot on Earth would simply swamp the sign you’re on the lookout for.”
So, the robot-installed lunar telescope should be on the Moon’s far facet, and since it’s simply on the lookout for a selected vary of low-frequency waves, it might be laborious for supporters to justify its value (within the ballpark of a pair to a couple billion {dollars}) compared to its utility to the bigger astronomical group.
“Nobody else within the astronomy division cares about it, apart from the few individuals who care about early universe science,” Bandyopadhyay added. “So this kind of journey forward for us is sort of laborious.”
Bandyopadhyay separated the sorts of science missions achieved off Earth into three courses: missions which might be uniquely possible from area, missions that use space-based devices in tandem with Earth-based devices, and science missions designed to maintain human beings alive in area. All three are in humankind’s plans, however the former two will probably be made simpler if the third is prioritized. Having people on website on the Moon, Mars, and maybe elsewhere thereafter will imply they will drawback remedy sooner than it takes Earth-based scientists to diagnose and remedy issues remotely.
To infinity and past?
With a bit of luck—and loads of planning—people will return to the Moon inside the decade. House businesses and business companions are creating the applied sciences essential to each get our species to Mars and permit for a sustainable, long-term presence on the planet. We’re an extended, good distance off from interstellar journey, however it’s not past the realm of chance.
“I believe I and lots of different individuals have a look at the Earth extra like a cradle,” Vermeulen mentioned. “It’s a place to begin. And there may be this magnificence in reaching out and connecting with the place we got here from—this large universe—and go deeper into that.”
The applied sciences of tomorrow are being designed as we speak, in order that people will probably be prepared when the expertise to journey past Earth and keep there exists. And even as soon as it does exist, we’ll must innovate on these applied sciences, make the manufacturing of those instruments cheaper, and make their designs extra intuitive and helpful, and so forth.
Proper now, transporting people to Mars is unfeasible; it’s an extended journey with a brief, intermittent launch window, and any ship carrying people would have to be correctly shielded from radiation.
“As soon as we determine that out, I believe people will actually be a planet-faring civilization,” Bandyopadhyay mentioned. “I might anticipate {that a} hundred years from now, we’d have bases on Moon and Mars. And to make all of that occur, it’s worthwhile to first work out the best way to make that occur.”
Generally it feels just like the march of spaceflight is sluggish, however even for all of the cautious work of individuals designing and launching missions, it really is transferring at a clip. You simply must step again to see how far more is being achieved as we speak than even 10 years in the past to comprehend that we’re on the cusp of a really new sort of area exploration, and all the brand new discoveries that may include it.
Trending Merchandise

Cooler Master MasterBox Q300L Micro-ATX Tower with Magnetic Design Dust Filter, Transparent Acrylic Side Panel, Adjustable I/O & Fully Ventilated Airflow, Black (MCB-Q300L-KANN-S00)

ASUS TUF Gaming GT301 ZAKU II Edition ATX mid-Tower Compact case with Tempered Glass Side Panel, Honeycomb Front Panel, 120mm Aura Addressable RGB Fan, Headphone Hanger,360mm Radiator, Gundam Edition

ASUS TUF Gaming GT501 Mid-Tower Computer Case for up to EATX Motherboards with USB 3.0 Front Panel Cases GT501/GRY/WITH Handle

be quiet! Pure Base 500DX ATX Mid Tower PC case | ARGB | 3 Pre-Installed Pure Wings 2 Fans | Tempered Glass Window | Black | BGW37

ASUS ROG Strix Helios GX601 White Edition RGB Mid-Tower Computer Case for ATX/EATX Motherboards with tempered glass, aluminum frame, GPU braces, 420mm radiator support and Aura Sync

CORSAIR 7000D AIRFLOW Full-Tower ATX PC Case – High-Airflow Front Panel – Spacious Interior – Easy Cable Management – 3x 140mm AirGuide Fans with PWM Repeater Included – Black








